Basics
- What Is Php?
PHP is a general-purpose scripting language widely used as a server-side language for creating dynamic web pages. Though its reputation is mixed, PHP is still extremely popular and is used in over 75% of all websites where the server-side programming language is known.
Hello World
echo function is used to display or print output
Comments
Commets are used to make the code more understandable for programmer, they are not executed by compiler or interpreter.
One Liner
This is a singleline comment
Another One Liner
This is a single-line comment
Multiline
This is a multiline comment
Vardump
This function dumps information about one or more variables.
Variables
Variables are "containers" for storing information.
Defining Variables
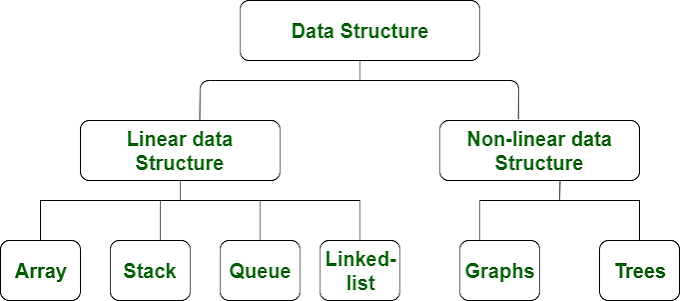
Datatypes
Datatype is a type of data
String
A string is a sequence of characters, like "Hello world!".
Integer
An integer is a number without any decimal part.
Float
A float is a number with a decimal point or a number in exponential form.
Array
An array stores multiple values in one single variable
Class
A class is a template for objects
Object
An object is an instance of the class.
Escape Characters
Escape sequences are used for escaping a character during string parsing. It is also used for giving special meaning to represent line breaks, tabs, alerts and more.
Line feed
It adds a newline
Carriage return
It inserts a carriage return in the text at this point.
Horizontal tab
It gives a horizontal tab space
Vertical tab
It gives a vertical tab space
Escape
It is used for escape characters
Form feed
It is commonly used as page separators but now is also used as section separators.
Backslash
It adds a backslash
Dollar sign
Print the next character as a dollar, not as part of a variable
Single quote
Print the next character as a single quote, not a string closer
Double quote
Print the next character as a double quote, not a string closer
Operators
Operators are symbols that tell the compiler or interpreter to perform specific mathematical or logical manipulations. These are of several types.
Arithmetic Operators
Addition
Sum of $x and $y
Subtraction
Difference of $x and $y
Multiplication
Product of $x and $y
Division
Quotient of $x and $y
Modulus
The remainder of $x divided by $y
Exponentiation
Result of raising $x to the $y'th power
PHP Assignment Operators
The PHP assignment operators are used with numeric values to write a value to a variable.
x = y
The left operand gets set to the value of the expression on the right
x += y
Addition
x -= y
Subtraction
x *= y
Multiplication
x /= y
Division
x %= y
Modulus
PHP Comparison Operators
Equal
Returns true if $x is equal to $y
Identical
Returns true if $x is equal to $y, and they are of the same type
Not equal
Returns true if $x is not equal to $y
Not equal
Returns true if $x is not equal to $y
Not identical
Returns true if $x is not equal to $y, or they are not of the same type
Greater than
Returns true if $x is greater than $y
Less than
Returns true if $x is less than $y
Greater than or equal to
Returns true if $x is greater than or equal to $y
Less than or equal to
Returns true if $x is less than or equal to $y
PHP Increment / Decrement Operators
Pre-increment
Increments $x by one, then returns $x
Post-increment
Returns $x, then increments $x by one
Pre-decrement
Decrements $x by one, then returns $x
Post-decrement
Returns $x, then decrements $x by one
PHP Logical Operators
And
True if both $x and $y are true
Or
True if either $x or $y is true
Xor
True if either $x or $y is true, but not both
And
True if both $x and $y are true
Or
True if either $x or $y is true
Not
True if $x is not true
PHP String Operators
Concatenation
Concatenation of $txt1 and $txt2
Concatenation assignment
Appends $txt2 to $txt1
PHP Array Operators
Union
Union of $x and $y
Equality
Returns true if $x and $y have the same key/value pairs
Identity
Returns true if $x and $y have the same key/value pairs in the same order and of the same types
Inequality
Returns true if $x is not equal to $y
Inequality
Returns true if $x is not equal to $y
Non-identity
Returns true if $x is not identical to $y
PHP Conditional Assignment Operators
Ternary
Returns the value of $x. The value of $x is expr2 if expr1 = TRUE. The value of $x is expr3 if expr1 = FALSE
Conditional Statements
Conditional statements are used to perform operations based on some condition.
If Statement
if statement checks the condition and if it is True, then the block of if statement executes; otherwise, control skips that block of code.
If..Else
if the condition of if block evaluates to True, then if block executes otherwise else block executes
If..Elseif..Else
It executes different codes for more than two conditions
Switch Statement
It allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values (cases).
Loops
Iterative statements or Loops facilitate programmers to execute any block of code lines repeatedly.
For Loop
It is used to iterate the statements several times. It is frequently used to traverse the data structures like the array and linked list.
Foreach Loop
The foreach loop loops through a block of code for each element in an array.
While Loop
It iterate the block of code as long as a specified condition is True or vice versa
Do-While Loop
This loop is very similar to the while loop with one difference, i.e., the body of the do-while loop is executed at least once even if the condition is False. It is an exit-controlled loop.
Predefined Variables
PHP provides a large number of predefined variables to all scripts. The variables represent everything from external variables to built-in environment variables, last error messages etc. All this information is defined in some predefined variables.
$GLOBALS
$GLOBALS is a PHP super global variable which is used to access global variables from anywhere in the PHP script.
$_SERVER
Returns the filename of the currently executing script. $_SERVER is a PHP super global variable which holds information about headers, paths, and script locations.
Returns the version of the Common Gateway Interface (CGI) the server is using
Returns the IP address of the host server
Returns the name of the host server (such as www.codewithharry.com)
Returns the server identification string (such as Apache/2.2.24)
Returns the name and revision of the information protocol (such as HTTP/1.1)
Returns the request method used to access the page (such as POST)
Returns the timestamp of the start of the request (such as 1377687496)
Returns the query string if the page is accessed via a query string
Returns the Accept header from the current request
Returns the Accept_Charset header from the current request (such as utf-8,ISO-8859-1)
Returns the Host header from the current request
Returns the complete URL of the current page (not reliable because not all user-agents support it)
Is the script queried through a secure HTTP protocol?
Returns the IP address from where the user is viewing the current page
Returns the Hostname from where the user is viewing the current page
Returns the port being used on the user's machine to communicate with the web server
Returns the absolute pathname of the currently executing script
Returns the value given to the SERVER_ADMIN directive in the web server configuration file (if your script runs on a virtual host, it will be the value defined for that virtual host) (such as someone@codewithharry.com)
Returns the port on the server machine being used by the webserver for communication (such as 80)
Returns the server version and virtual hostname which are added to server-generated pages
Returns the file system based path to the current script
Returns the path of the current script
Returns the URI of the current page
$_GET
PHP $_GET is a PHP super global variable which is used to collect form data after submitting an HTML form with method="get".
$_POST
PHP $_POST is a PHP super global variable which is used to collect form data after submitting an HTML form with method="post". $_POST is also widely used to pass variables.
$_REQUEST
PHP $_REQUEST is a PHP super global variable which is used to collect data after submitting an HTML form.
Variable-handling Functions
The PHP variable handling functions are part of the PHP core. No installation is required to use these functions.
boolval
Boolval is used to get the boolean value of a variable
isset
It is used to check whether a variable is empty. It also checks whether the variable is set/declared:
unset
It unsets variables.
debug_zval_dump
debug_zval_dump is used to dump a string representation of an internal zval structure to output
empty
Empty is used to check whether a variable is empty or not.
floatval
It returns the float value of different variables:
get_defined_vars
It returns all defined variables, as an array:
get_resource_type
It returns the resource type:
gettype
It returns the type of different variables:
intval
It returns the integer value of different variables:
is_array
To check whether a variable is an array or not:
Array
An array stores multiple values in one single variable.
Declaring an Array
Functions
A function is a block of statements that can be used repeatedly in a program
Defining Functions
MySQLi Functions
These functions allow you to access MySQL database server.
mysqli_connect() Function
It opens a non-persistent MySQL connection
mysqli_affected_rows() Function
It returns the number of affected rows
mysqli_connect_error() Function
It shows the Error description for the connection error
mysqli_fetch_all() Function
It fetches all result rows as an array
mysqli_fetch_array() Function
It fetches a result row as an associative, a numeric array, or both
mysqli_fetch_assoc() Function
It fetches a result row as an associative array
mysqli_fetch_row() Function
It fetches one row from a result set and returns it as an enumerated array
mysqli_kill() Function
It kills a MySQL thread
mysqli_close() Function
It closes a database connection